What is Methanization ?
In order to bounce back on our two previous articles on permaculture, let us remain in this perspective of optimizing our ecosystem in order to reduce our ecological footprint. Thus, we will see in this new article the concept of Methanization. Methanization is a biological process of organic waste treatment leading to a combined production of gas convertible into energy (biogas) and a digestate usable as compost. Methanization appeared at the end of the 17th century, in 1776 with the discovery of methane by Alessandro Volta. This Italian scientist identifies the existence of “carbonated hydrogen gas” in the gas bubbles emitted by rotting vases. This is how he highlighted the flammable aspect of “marsh gas”, demonstrating the high methane content resulting from the decomposition of organic plant waste from swamps.
The Brundtland Report defines sustainable development as “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs”. This duality between current consumption and preservation of the environment for future generations leads us to question our societal model. If we follow this reasoning, our way of consuming and using techniques to take advantage of the earth’s natural resources is obsolete, even archaic. Improving our techniques is essential to meeting our needs in a sustainable and viable manner.
Indeed, innovation could spearhead this sustainable development strategy in order to change our societal model and be part of green ecological growth. In this context, methanization is perfectly in line with this perspective: innovative, environmentally friendly and efficient, it could play an essential role in this energy transition.
How does the Methanization works ?
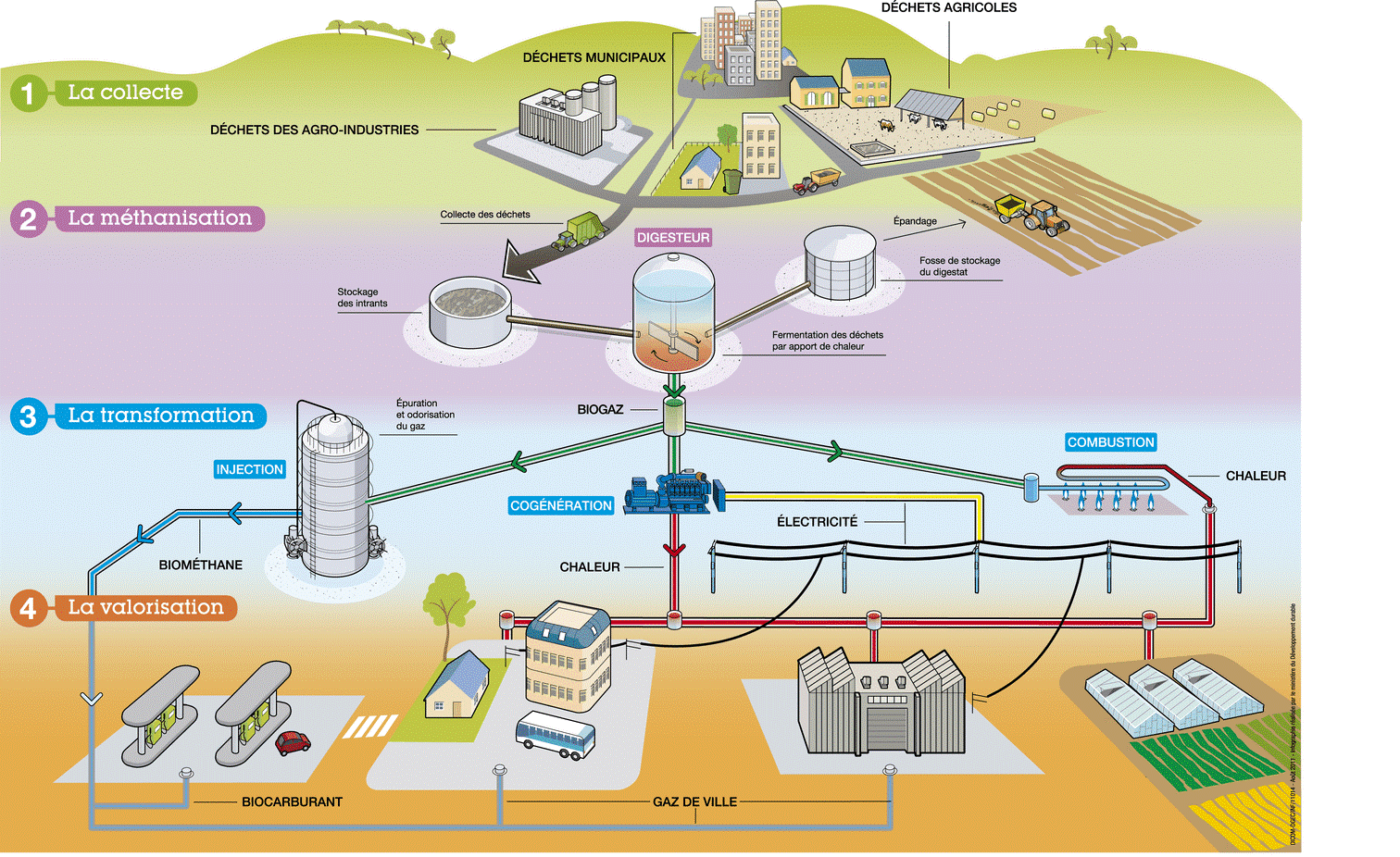
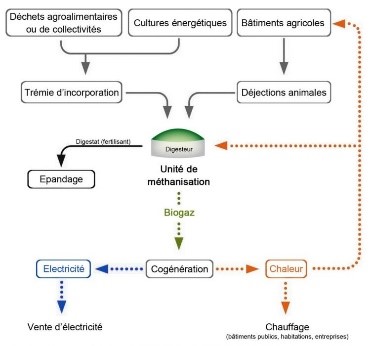
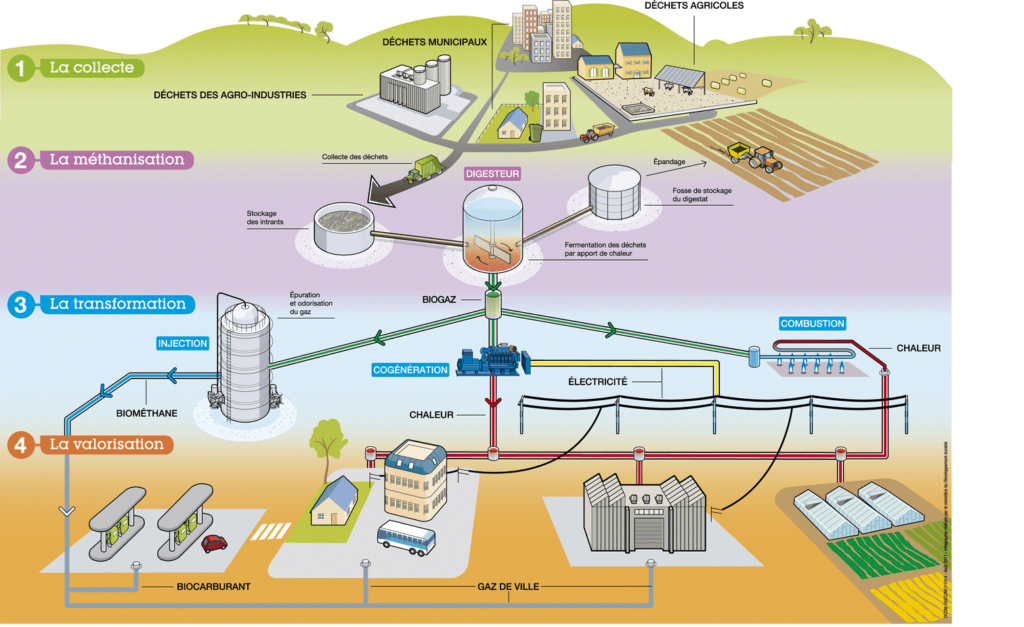
The principle is as follows: degradation of organic matter in an oxygen-free environment. Indeed, the organic waste is stored in a cylindrical and hermetic tank called “Digester”. In which organic waste is subjected to the action of micro-organisms (bacteria) anaerobically (absence of oxygen). Biogas production is then the result of 4 biochemical stages in which large carbon chains are transformed into fatty acids and alcohols. This methane fermentation leads to a combined production of biogas convertible into renewable energy (composed of methane and carbon dioxide) and digestate. Finally, after the creation of biogas this energy to be recovered in different ways. Biogas can be used to produce electricity, heat and fuel for vehicles. But also as compost using digestate.
All organic matter is potentially decomposable. However, the methanization principle is better suited to water-rich substances, more easily degradable and easy to pump to allow continuous operation of the digester.
Organic waste is from:
- Agriculture: slurry, manure, crop residues, milking parlour water, grape marc.
- Agro-industrial: slaughterhouses, effluents from cellars, dairies, cheese factories
- Communities: mowing, sewage sludge
Major issues
Economic issues
In an economic logic, adopting a system of biogas production from organic matter will initially provide additional income from the sale of biogas. The treatment of organic matter then becomes a new revenue opportunity.
If the farmer does not wish to sell his biogas production, he can nevertheless use it and replace his traditional energy sources with biogas consumption (electricity production, fuel).
Storage and packaging savings will also be important. The transformation into digestate allows a significant reduction in the costs related to the management of organic matter. A farm will therefore hardly have to worry about managing the excreta on its farm. The digestate, on the contrary, is much more assimilable by living organisms.
Finally, it should be noted that organic matter is very abundant, so with methanization it becomes a profitable option that is also more respectful of the environment.
Environmental Issues
Indeed, methanization releases fewer greenhouse gases such as nitrous oxide. Thus, biogas production is significantly less polluting than that of”conventional” fossil energy. Biogas is also essentially a renewable energy source, which allows it to be a credible source of energy with a much smaller carbon footprint than traditional energy production techniques.
Conventional waste management has also been disrupted by this new process: organic matter management can now be viable and designed over the long term because it fits into a treatment and transformation scheme.
If methanisation is still in its infancy in France, we can see there a viable, profitable and less polluting solution of energy production than what is done today in the great majority of cases.
We hope you liked this article, do not hesitate to ask us questions if you have any, we will be pleased to answer you. We invite you to visit our ranges of ecological bags in order to remain in this approach of respect for the environment and a better use of our techniques.
References :
https://sms.hypotheses.org/9386
https://theconversation.com/innovations-dans-le-traitement-des-dechets-la-methanisation-69572
http://www.biogaz-energie-renouvelable.info/methanisation_avantages.html
https://www.actu-environnement.com/ae/dictionnaire_environnement/definition/methanisation.php4